How is the friction orientation of both hard and soft LCD screens?
09.26.2023
The relationship between hard and soft LCD screens:
1: LCD hard and soft screens: refers to the technical differences between the screens
Hard screen mainly refers to IPS technology, just started by Hitachi and other Japanese manufacturers to implement, and later LPL significantly improved, constituting S-IPS hard screen process technology, also known as super IPS technology or second-generation IPS technology. TN, PVA, MVA and other panels belong to the soft screen, a representative manufacturer is Samsung, Sharp and Taiwan Province panel manufacturers. The basic difference between the two is the different approaches to placing the liquid crystal molecules. Hard screen does add a layer of hard maintenance outer film on the LCD panel, but this is not the basic difference. When there is a difference between a soft screen and a hard screen, you can use your finger to quietly tap or press the screen. If a shadow is presented, it is a soft screen, otherwise it is a hard screen. Because of the LCD screen, there is a layer of liquid crystal at the back, and a shadow will appear after a subtle press.
Visually, there is no obvious interval between several techniques, all between 170-180 degrees; in terms of operating life, the two are similar; in terms of energy consumption, the first thing to look at is the backlight, circuitry, etc, not due to the panel soft or hard; in terms of safety performance, there is no basic difference between hard screen and hard film. The difference between the two mainly lies in the response speed and contrast. IPS hard screen response is faster, dynamic picture performance is relatively outstanding, but in contrast performance is relatively poor. It should be noted that the difference between the two is theoretically formed by the different placement of liquid crystal molecules, detailed to the product, but also vary depending on the capacity.
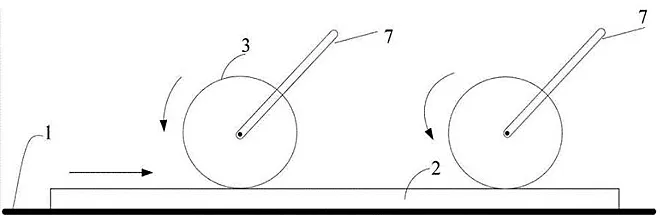
2. The principle of LCD friction orientation
LCD orientation layer can be formed by rubbing the orientation film along a direction with a flannel. Take the orientation layer of the liquid crystal molecules will be placed parallel according to the friction direction, so as to be able to complete the common orientation. The upper and lower sheets of liquid crystal molecules are placed at 90 degrees to each other, which is the central link in the manufacture of twisted column phase liquid crystal box. The principle of frictional orientation is still debated, but one thing is certain, that is, when the liquid crystal molecules are placed along the frictional direction, the system has the lowest energy, or the liquid crystal molecules of the orientation layer tend to be placed along the direction of the lowest energy, which is called the anchoring energy. As for the friction gives the microscopic mechanism of the placement direction, can be thought of from the following two aspects: First, the depth and width of the dense groove is "planed" by friction, the two ends of the groove is different. If the process of planing is used as an analogy, one end of the groove is wide and deep, and the other end is narrow and shallow. Such grooves, especially those with appropriately sized liquid crystal molecules (nanoscale), are bound to have an effect on the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules. Another consideration is the effect of the orientation direction of the organic polymer on the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules.

